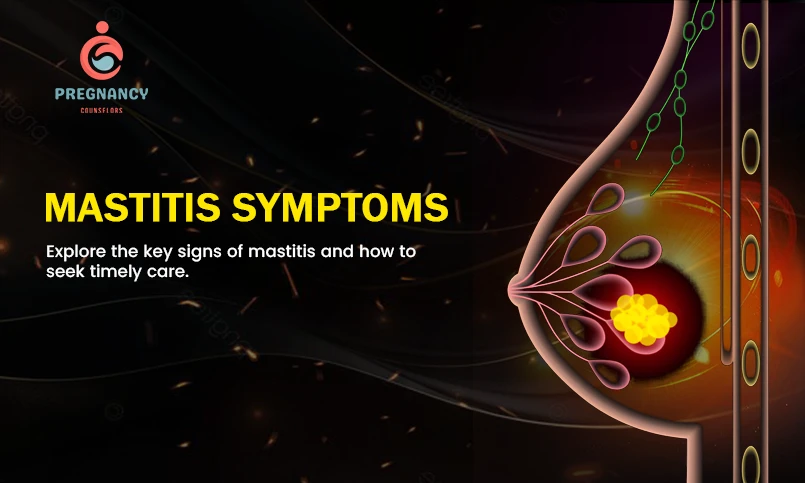
Mastitis is an inflammatory (swelling or redness) condition of the breast tissue that develops due to bacterial infection. The mastitis condition generally occurs in breastfeeding women, but it can also be seen in many non-breastfeeding women, men and children as well in lesser cases. Understanding the mastitis symptoms, treatment and causes will help to manage the issue and reduce the chances of further risk. Mastitis results in discomfort, pain, swelling and redness on the breast. To understand what mastitis symptoms are & How to treat and Prevent Mastitis check the details and information’s below.
Types of Mastitis
Mastitis is classified into two categories on the basis of breastfeeding conditions.
- Lactational (breastfeeding-related) Mastitis
- Non-Lactational Mastitis
Lactational Mastitis
The lactational mastitis occurred because of the blockage of the milk duct, when the breast milk doesn’t pass properly from the breast or the bacteria from the skin of the baby or the mouth enter the breast tissue from the cracks or sore nipples. This generally happened to the
The condition arises when the breastfeeding is improper: blockage in the milk duct, increased in milk production, poor latching, damaged or cracked nipples, and more.
Non-Lactational Mastitis
The non-lactational mastitis can occur in women who are not breastfeeding, in men and even in children. Mastitis may be caused by a blocked duct, an injury, an abscess (a localized collection of pus in the breast tissue that can occasionally be caused by bacterial infections), or even breast cancer.
Certain risk factors, including obesity, smoking, nipple piercings, prior breast surgery, and diseases like diabetes, can cause the condition.
Mastitis Symptoms
Mastitis symptoms generally develop quickly and vary in intensity. Here is the list of mastitis symptoms.

Pain and Tenderness
The most common mastitis symptom is concentrated pain and tenderness in one part of the breast. The pain begins with the light ache and starts becoming sharper and more painful with the infection’s growth. It is easy to recognize the mastitis symptom in the lactational mastitis type during or after breastfeeding when the breast swells or redness occurs.
The infected area of the breast looks swollen, warm, harder and red and can easily be noticed as the mastitis symptoms. The skin, which frequently has a wedge-like shape, may appear “patchy” red.
Lumps or Hardness
Mastitis symptoms may include feeling a hard or firm lump in the breast. This may be the result of milk accumulation from a blocked duct or an abscess, which is a collection of pus.
Additionally, the lump may feel tender to the touch and occasionally be mistaken for a blocked milk duct.
Fever and Flu-like Symptoms
One of the mastitis symptoms is fever, which usually occurs above 101°F or 38.3°C. Systemic symptoms of mastitis include chills, body aches, and general exhaustion because the infection triggers the body’s inflammatory response. These mastitis symptoms may appear suddenly and can be severe, making the person feel unwell and fatigued.
Nipple Discharge
Discharge from the nipple, especially if it’s pus-like or contains blood, can indicate the mastitis symptom and generally happens due to an abscess having formed.
Warmth
Because of the tissue’s inflammation and infection, the afflicted breast will feel warm or hot to the touch. And sometimes the women may feel the burning sensation.
Painful or Difficult Breastfeeding
Feeling uncomfortable and painful while breastfeeding is one of the major mastitis symptoms. When nursing or expressing milk, women who are nursing may experience pain that gets worse. Reduced milk production from the afflicted breast due to discomfort may exacerbate the blockage and raise the risk of an abscess.
Mastitis Symptoms Risk Factors
Mastitis symptoms happen because of the bacterial infections, usually from Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus, which can enter the breast tissue through broken skin (e.g., cracked nipples) or clogged milk ducts. Here are the major risk factors that occurred due to mastitis.
- Blockage of Milk Ducts: This risk factor occurs when the breast doesn’t excrete milk properly and it creates a blockage in the milk duct. This condition will lead to the infection.
- Due to the entry of the bacteria through the cracked or sore nipples that further reach to the milk duct and grow the bacterial infection.
- Engorgement of breast or insufficient breastfeeding or pumping can result in milk backing up into the breast tissue, which may result in infection.
- During breastfeeding, a poor latch can result in milk stasis and prevent the breast from emptying completely, increasing the risk of mastitis.
- Both emotional and physical stress can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight against the infection.
Diagnosis of Mastitis

Diagnosing the mastitis symptoms to confirm the issue and have the treatment before it grows intense and results in more issues. Diagnosis can be done with the help of the following methods.
- In a physical examination, the doctor or the healthcare provider will examine the breast for mastitis symptoms such as redness, swelling, lumps, or abscesses.
- The doctor will also look forward to the breastfeeding habits, nipple conditions or any history of the breast surgery or the infections.
- Checking the mastitis symptoms condition with the help of ultrasounds to check whether it is filled with pus or not. For the non-breastfeeding women, mammography is done to check for rare conditions such as breast cancer and more.
- Going for the lab-related test, including the milk culture and blood test.
Treatment for Mastitis Symptoms
The treatment for mastitis symptoms involves various methods that can reduce the risk factors and can also cure the issue. Here are the following ways the healthcare provider will suggest.
- Using antibiotics to heal the mastitis symptoms or the infection completely. It is recommended to follow the proper duration or course of medication prescribed by the healthcare provider.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers can help reduce pain and inflammation, but consult the doctor for the full recovery.
- In addition to reducing pain, applying warm compresses to the afflicted area may facilitate milk flow.
- It is critical to keep nursing or pumping because this lowers the risk of abscess formation and helps drain the contaminated milk. Pumping can be a good substitute for breastfeeding if it hurts. Regular breastfeeding may promote quick healing and relieve milk stasis.
- An abscess may form and need to be drained. This can be accomplished by making a tiny cut or, in certain situations, by aspirating a needle. A doctor typically performs this procedure in a clinical setting.
- Sufficient sleep, hydration, and nourishment boost the immune system and hasten the healing process.
Prevention for Mastitis Symptoms
There are numerous possible ways to prevent or reduce mastitis symptoms and its risk factors.
- During breastfeeding, make sure the infant latches well to facilitate efficient milk drainage.
- Regular nursing or pumping will help avoid milk accumulation. Avoid the long gaps in between the breastfeeding’s to manage the issue.
- Maintain cleanliness and dry the nipples after feeding and during the breastfeeding phase to prevent soreness or cracking.
- Tight clothes will reduce milk production. Therefore, it is recommended to wear loose clothes or maternity clothes to avoid the risk of clogged ducts.
- Get adequate sleep, manage your stress, and preserve your general health in order to boost your immune system.
FAQS
How do I know if I’m getting mastitis?
Only one breast is typically affected by mastitis, and symptoms frequently appear rapidly. The mastitis symptoms include a swollen area on the breast that may feel hot and painful to touch.
What is the best treatment for mastitis?
Antibiotics and milk removal from the breast are the usual treatments for mastitis. However, in rare cases, it is resolved with the help of surgery.
What happens if mastitis is left untreated?
Pus can accumulate in the breast as a result of untreated mastitis or a blocked milk duct or can result in breast cancer.
What is the main cause of mastitis?
An excess of milk, or hyper lactation, is the most common cause of mastitis.