When fertilization of an egg by sperm happens originates from males and females to create a new zygote. The essential biological process maintains species continuity and seeds the developmental origins that fuel new organism development. The research built on life science demands an extensive understanding of fertilizer for examining life origins while tracing genetic inheritance and investigating species evolution. Learning about fertilized eggs gives researchers insights into reproductive health while promoting their understanding of how genetic diversity operates. The acquired understanding plays an essential role for driving medical treatment forward while enhancing reproductive success throughout the world.
The Biological Basis of Fertilization
The union of male sperm cells with female eggs occurs in appropriate conditions leading to fertilizer. Human fertilizer takes place inside the fallopian tubes during monthly reproductive activity. Scientists commonly wonder about the precise timing of fertilization. Under favorable circumstances fertilization takes place directly after ovulation when the egg and sperm successfully meet each other.
The fusion of sperm with the egg develops into a diploid zygote by bringing together two haploid cells that contain half the genetic components each.They share one set of complete chromosomes. Structurally this new organism begins development as the first cellular stage within the zygote. The combining of DNA between egg and sperm creates new genetic combinations which results in both reproductive potential and distinct offspring characteristics.
The Process of Fertilization in Humans
Sperm Transport and Capacitation
During ejaculation sperm cells travel to the female reproductive area along with millions of other sperm cells. Spermatic cells must travel through mucous tissue to access the fallopian tubes to perform fertilization. Sperm cells require capacitation during this time because this process turns them into egg penetration-ready.
The central question that people frequently ask concerns the specific indicators which show sperm successfully fertilizing the egg. After successfully fertilized triggers immediate biological changes within the female body that occur without physical indicators.
Egg Release and Transport
When ovulation occurs one of the ovaries releases an egg which the fallopian tube’s fimbriae captures. After release from the ovary an egg remains capable of being fertilized in a period of twelve to twenty-four hours. The key period enables the determination of when fertilization can occur.
Sperm-Egg Binding
For sperm to be fertilized on an egg these reproductive cells must successfully penetrate all protective layers surrounding the egg such as the zona pellucida along with the corona radiata. Enzymes originating from the sperm’s acrosome enable their penetration into egg layers.
Fusion and Zygote Formation
When is fertilization happening? Membrane fusion occurs at exactly the moment when one fertilizes of an egg by sperm. With zygote formation, the sperm nuclei unite with those of the egg to finalize the sperm-fertilized eggs throughout this process.
Types of Fertilization
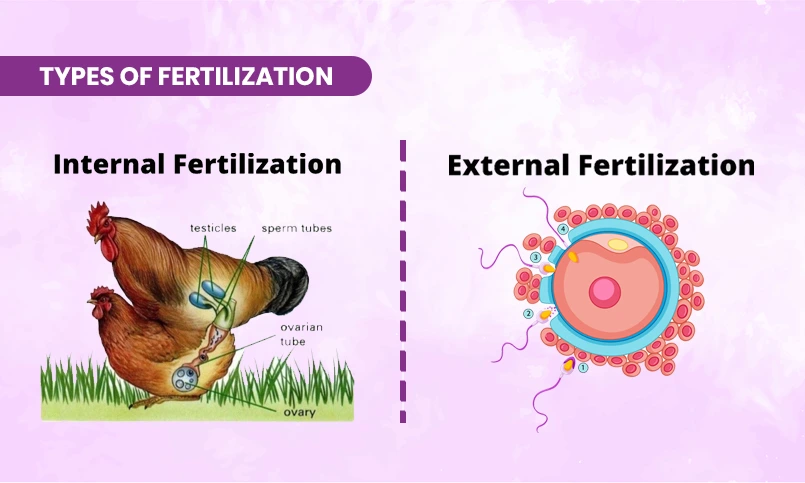
Internal Fertilization
The reproductive process takes place internally within a female body for humans along with mammals as well as numerous other species. The developing zygote enjoys safety under the controlled conditions of this procedure. The success rates of internal fertilization require fewer gametes than the procedure of external fertilization. Through this method, a protected environment enables efficient sperm fertilization.
External Fertilization
External fertilization happens outside of bodies according to aquatic species such as fish along with amphibians. Both gametes leave the body during release before partner sperm joins egg cells within aquatic surroundings for fertilize. Few offspring survive through this approach because environmental threats as well as predators decrease the method’s success rates despite its capability to create numerous offspring.
Signs of Sperm Fertilizing Egg
Many individuals wonder about the signs of sperm fertilized eggs. During the early phases of pregnancy internal biological signs primarily indicate conception. After fertilization takes place hormone levels start to change including the sharp increase of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin). The fertilized egg’s bond toward the uterus wall also reveals itself through implants bleeding and a permanent rise in basal body temperature.
Assisted Reproductive Techniques (ART)
Modern medical techniques provide ART solutions for people who face difficulties with natural methods of fertilized. These methods mimic the natural processes of fertilized eggs with sperm in controlled environments:
In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
When fertilization is done outside of the human body by mathematical experts, putting sperm and eggs together. After successful fertilization, the embryo then travels to the uterus for direct implantation.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
If the male’s fertility requires fertilization then doctors inject one sperm directly into an egg using an assisted procedure.
Artificial Insemination
In an attempt to increase the chances that sperm fertilized eggs, medical staff put sperm into the female reproductive system.
Despite struggling with infertility, fertilization prediction techniques allow couples to understand their most likely timing and bring them reassurance.
Fertilization in Plants
Through the union of male gametes (pollen) with female gametes (ovules), plants are able to become reproductive successes. The vehicles for the pollen travel to the stigma include wind, water and bee pollinators. During plant life the female plant and the male plant releases sperm in the female plant, this sperm fertilized egg in plant life creates seeds that sustain life of both species and agricultural biological diversity.
Factors Influencing Fertilization
In both natural and assisted reproductive settings, egg and sperm fertilization success rates are impacted by multiple conditions. By matching these factors, we are able to set the conditions needed for sperm fertilization of the eggs. Below are the main factors that influence the fertilize process:

Timing
Precise timing is the only thing that is key in resulting in the successful outcome of fertilization. The time inside the female reproductive system where male reproductive cells remain viable stretches to five to seven days up until the egg is released for ovulation. This means fertilization needs to happen successfully during the 12-24 hour period following the egg’s release during ovulation. Proper timing of egg retrieval procedures and sperm delivery maintenance continues to be crucial for achieving high success rates in In Vitro fertilize.
Gamete Health
For the sperm to fertilize she must have excellent sperm quality and egg quality as well. Successful penetration into the egg requires the three key features of sperm functionality: movement and shape and genomic health. Egg quality declines throughout human aging and this leads to poor fertilization success. Egg and sperm quality which completes fertilisation successfully is a result of the combined effects of both, lifestyle decisions and dietary patterns and health parameters.
Environment
When we reproduce naturally, a good environment in the reproductive tract allows sperm and egg to meet. Ovulation is the time when the mucus from the cervix helps sperm to move towards the egg to get it fertilized inside of the fallopian tube. Methods such as IVF take place under controlled lab conditions where we have the perfect temperature and pH condition for successful fertilization to occur.
External Conditions
Fish as well as amphibians with external fertilization must rely on ideal water temperatures and pH levels and pollution-free conditions for successful reproduction. At the proper temperature sperm function better and eggs remain more viable while changes to pH or pollutants interfere with the fertilize process. The reproductive success of external fertilize species depends completely on optimal external conditions.
Ethical and Social Considerations
The discussion of the ethical dimensions and social consequences of assisted reproductive technology (ART) methods extends along with the spread of these methods. Issues such as embryo selection, accessibility, and affordability of treatment raise questions. Various cultural groups accept ART methods as infertility solutions while others dislike them. The development of reproductive healthcare solutions needs to ensure its technology based and value (ethic based) derived protocols but in harmony problems and challenges arise.
Conclusion
Like all life forms, the processes of fertilization perform dual roles in reproductive development. In terms of biology and medicine, sperm-egg combinations allow the conservation of a species, while yielding genes that do not correspond from parent to child.
Since fertilization involves factors such as its timing and relating to eggs and sperm cells that produce visible evidence, analyzing fertilization needs an idea of what it is. The process of life going on forever ensures sperm fertilizes an egg between natural methods and Assisted Reproductive Technologies. While the diploid chromosome number of the organism is restored for proper development a new organism begins to form during egg sperm fertilization.
The improvements in in-vitro fertilization (IVF) and other Assisted Reproductive Technologies give us a unique opportunity to see and offer strategies to help people through their fertility difficulties. New technological advances that function both as a ray of hope and demonstrated how human caring is gradually being brought together with advances in engineering.
The ability to understand when fertilization happens and to control these mechanisms deepen both our understanding of complex biological functions and new reproductive medical science achievements.

