Fetal arrhythmia is a condition of the heart where the rhythm of the heart decreases or lowers in a developing baby as per the standard heartbeat rate. In simple terms, it is an irregular heartbeat condition in an unborn baby. The irregular heartbeats mean the baby is not getting enough oxygen or having other issues, which are generally curable.
The issue is identified or detected during the regular or routine checkup of the pregnancy phase. Although the issues are mostly impermanent and not harmful because the fetus sometimes changes the heart rhythm as per the response to the condition of the uterus, but the issues need proper attention and medication to cure the issue at the beginning level.
In addition, the baby’s heartbeat becomes erratic during the second trimester as the heart’s electrical pathways develop. Unless the irregularities occur for a long time, this is considered normal and should not raise any issue.
Fetal Arrhythmia Causes
There are various causes of the fetal arrhythmia, from which major causes are controlled or managed by the mothers to avoid such issues.
- Maternal conditions like thyroid issues, diabetes, infections or more.
- Fetal structural abnormalities with heart problems cause congenital heart defects (CHDs), which is considered the most common type of birth heart defect.
- Prescribed medication or toxic substance exposure during pregnancy.
- Genetic conditions are the major reason for the fetal arrhythmia.
- Chromosomal abnormality in the family or to the parents, such as Down syndrome or Turner syndrome, can also affect the heart condition of your little life.
- Electrical signals from the heart can be the reason for causing problems.
- Restricted blood flow to the heart, or ischemia (it is a condition when the blood flow is blocked or restricted to the specific parts of the body).
- Electrolyte imbalance can lead to major maternity complications that also include premature birth, birth defects, fetal arrhythmia, anxiety during pregnancy and more.
- Hypoxia ( low oxygen level)
Types of Fetal Arrhythmia
Tachycardia: it is a heart condition in which the heartbeat runs faster than the normal BPM (beat per minute). Fetal tachycardia refers to when the fetus’s heart rate goes above the normal range, which is generally from 110 to 160 beats per minute.
Fetal tachycardia is of two types.
- Mild Tachycardia: Heart rates between 161 and 180 beats per minute are considered under the mild tachycardia.
- Severe tachycardia: the heartbeat rate that goes above 180 bpm.
Bradycardia: when the heartbeat rate is slower than the normal heart rate.
Fetal bradycardia is a condition generally defined as a sustained fetal heart rate below 110 beats per minute (bpm) for a period of time in a developing baby. Depending on its cause and duration, it can be a potentially dangerous condition that could be a sign of fetal distress or other underlying problems.
Normal Fetal Heart Rate
The normal fetal heart rate is typically 110 to 160 bpm. However, there are temporary heart rate fluctuations that can occur during the labor or due to other external reasons and are not always a cause for concern.
Types of Fetal Bradycardia
- Mild Bradycardia: when the heart rate is detected between 100 and 110 bpm, which may not always be concerning if not regular or for a long period of time.
- From mild to severe Bradycardia: A heart rate below 100 beats per minute, particularly if it persists.
Fetal Atrial Flutter or Fibrillation: it is a rare condition but may indicate more serious arrhythmias.
Irregular Beats: Irregular beats occur in abnormal heart rhythms where the heartbeat may be too fast, too slow, or irregular. In developing babies, the condition of irregular heartbeats can sometimes be detected during routine monitoring or ultrasound. While in most of the cases this condition resolves on its own, others may indicate basic issues. This issue is often caused by premature atrial contractions (PACs), which are usually not a serious issue.
Types of Fetal Irregular Heartbeats
- Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs): it is the most common type of fetal irregular heartbeat. Generally occurs when the atria (upper chambers of the heart) beat earlier than normal. Most of the time this condition cures without any
- Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs): this condition is caused by early electrical impulses originating in the ventricles (the lower chambers of the heart). These extra beats interrupt the normal heart rhythm and can be detected or monitored in both adults and fetuses.
Rapid and irregular heartbeat rhythms (e.g., supraventricular tachycardia), these conditions can lead to complications like fetal heart failure if they occur for a long period of time.
Fetal Arrhythmia Complications
Due to the fetal arrhythmia condition, the pregnancy has many complications, such as.
- The condition will leave a huge impact on fetal development.
- In serious or severe conditions, it can develop the risk of heart failure.
- Prematurity-related issues such as premature birth.
- Fetal heart failure.
- Stroke
- cardiac arrest
Symptoms of Fetal Arrhythmia
Early signs and symptoms of the fetal arrhythmia that can be identified and detected easily during the beginning of the condition.
- Irregular fetal movement patterns.
- Reduced fetal heart rate.
- Such as a slow or irregular heartbeat or notice pauses between heartbeats. You may also feel like your heart is skipping a beat, fluttering, pounding, or beating too hard or too fast.
Other symptoms cover below measures that can or cannot be the reason for the issue.
- Anxiety
- Chest pain or discomfort while breathing or gasping during sleep
- Difficulty in breathing.
- Dizziness and fainting
- Tiredness or weakness
Importance of heartbeat monitoring
It is important to measure the heartbeat rhythm of the fetus, especially if the pregnancy is in a high-risk condition. The average fetal heart rate is between 110 and 160 beats per minute.
Fetal Arrhythmia Diagnosis
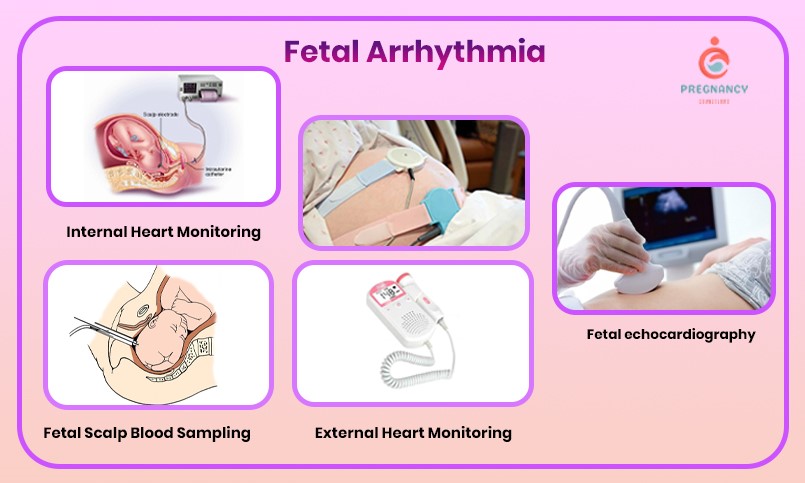
There are two major ways to monitor the fetal heart beat (Internal and External)
- Internal Heart Monitoring: during the internal heart monitoring, the healthcare provider or doctor. In Internal Heart Monitoring, a thin wire (electrode) is placed on the baby’s scalp through the cervix of the mother. The wire is connected to the monitor machine.
This method of heartbeat monitoring can only be done if the cervix is open and the amniotic sac is broken (repurture of membrane) during the labor. The healthcare provider will also monitor the uterine contraction.
- External Heart Monitoring: The external heart monitoring is done with the help of cardiotocography (CTR), portable heart rate monitoring devices, or Doppler ultrasound.
A transducer (sensor) is placed on the mother’s abdomen to perform the external heart monitoring. It can be done during the regular checkups and labor time.
CTR: The CTR is a continuous monitoring method, and it is also beneficial for finding or detecting distress, generally done during late pregnancies or labor time. This method majorly measures the heart rate pattern and the uterine contraction. Two external transducer is used during the process
Other methods of fetal heartbeat monitoring.
- Fetal echocardiography: this method is used to measure the structure, function, and blood flow. It is generally performed during the high-risk pregnancies, during the second trimester, or if congenital heart defects are suspected. It is considered the most accurate external heart monitoring as it is diagnostic-grade imaging.
- Non-Stress Test (NST): it is generally considered under the routine checkups and requires measuring the heart rate in response to the fetal movement. A single transducer is used while performing the Non-Stress Test.
- Fetal Scalp Blood Sampling: A small amount of blood is extracted from the scalp of the baby inside the fetus to measure oxygen and pH levels. It is used to measure whether the fetal is stressed during the labor or not.
- The biophysical profile (BPP) is calculated by combining an NST and an ultrasound to determine the fetal heart rate, breathing, movement, muscle tone, and amniotic fluid levels. This method is considered simple and painless.
Fetal Arrhythmia Treatment
The fetal arrhythmia treatment requires regular monitoring, medication and proper planning.
- Monitoring: having regular or routine prenatal checkups, especially during the second and third trimesters of the pregnancy, is essential.
During the monitoring, the healthcare provider will check the level of concern and determine how much time and medical assistance are required to cure the issue.
- Medications: the mothers should not avoid medications. Stick to the prescribed medications, as it will help to cover the condition quickly. Additionally, also focus on the maternal health conditions to avoid such issues.
- Delivery Planning: keep yourself updated with the change of medications or other necessities during the pregnancy.
- Avoid the usage of harmful substances during pregnancy. Toxic substances or a bad diet can also become one of the reasons.
- Rare conditions of fetal arrhythmia require in utero treatment.
- Postnatal care of the baby is essential.
- Surgery can be performed or pacemakers for congenital issues.
If fetal arrhythmia is detected, maintain open communication with a healthcare provider or the doctor to avoid other complications and issues to the baby’s health.
Preventions
- Stick to diet plans and manage the lifestyle, as they are the key reasons for any condition during the pregnancy phase.
- Avoid toxic substances such as smoking, drinking, and more.
- Consult the healthcare provider for any queries or assistance.
- Follow the routine prenatal checkups.
- Have open communication with your healthcare provider or the pregnancy counselors and take guidance about the issues and queries.
- Keep yourself educated on the conditions and measures that can occur during the pregnancy.
Early diagnosis of the fetal arrhythmia can help the healthcare provider to provide better assistance and manage future issues that need to be cured. Moreover, it requires more care and support. Mothers should have a clear conversation with their healthcare provider to help them diagnose the condition and the depth of the cause.
With advanced medical science, the fetal arrhythmia is easily managed and cured with proper care and support.
FAQS
Is a heart arrhythmia serious?
Arrhythmias can cause damage to the heart, brain, and other organs if not treated properly. This can result in life-threatening strokes, heart failure, premature deaths, heart defects or cardiac arrest. The condition can extend to a life-threatening issue and stay even after the healthy birth if not diagnosed and cured in the beginning.
What causes arrhythmia in pregnancy?
The exact issue or reason because of which the arrhythmia occurs or rises during pregnancy is unidentified, although it is assumed that bad diet, exposure of toxic substances, stress, genetic disorders and other issues are the major reasons for the arrhythmia in pregnancies, but adaptive cardiovascular, hemodynamic, and autonomic changes appear to be the primary drivers. Cardiovascular changes, including increased cardiac output and blood volume, as well as reduced systemic vascular resistance and blood pressure, are also defined as the reasons for the problem.
How can arrhythmia be treated?
The arrhythmia can easily be treated if deleted at the beginning of the issue. The common treatments for the arrhythmia cover medicines, surgery to implant devices that control the heartbeat rhythm, and other procedures or methods to treat problems with electrical signals in the heart. Although the concern is related to the developing baby during the pregnancy phase, mothers should have proper medication, regular checkups, should avoid the toxic substances, and should have open communication to avoid risk and further complications.